Hikers Who Love Wildlife Should Visit Wyoming's Underrated National Monument In The Fall
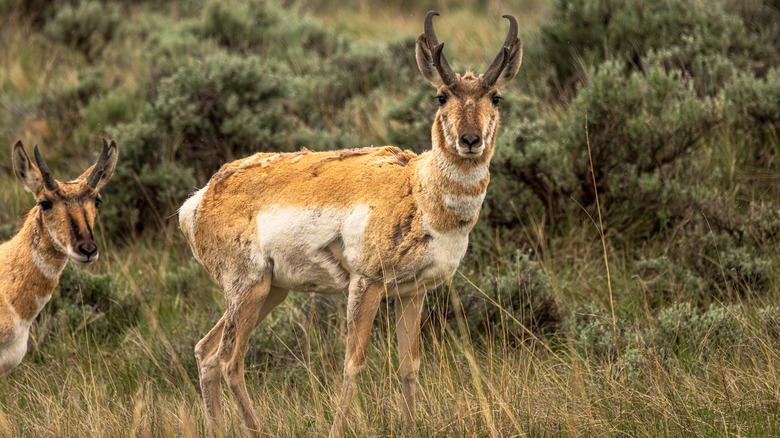
If you don't live in Wyoming, the sight of a pronghorn antelope is positively magical. These thickly-coated mammals are like a cross between a deer and a wild goat, and look so peaceful as they graze in western grasslands. Yet the moment they're startled, a pronghorn springs into action, sprinting up to 60 miles per hour across the plains. When you spot a pronghorn on the move, you believe it's the speediest land animal in North America. They're also an evolutionary oddity; they look a lot like African antelopes, but they're genetically unrelated. Believe it or not, their closest relatives are giraffes.
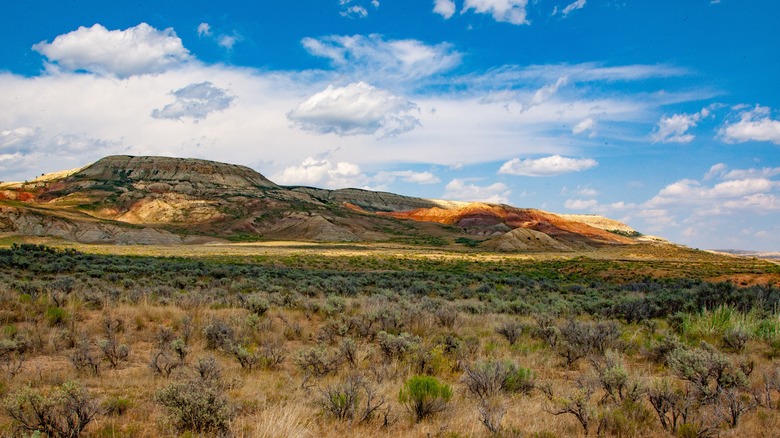
This is just one species you may spot in the scrubland around Fossil Butte National Monument. Shaped like a giant, striated bottle cap, Fossil Butte is a big hill composed of sedimentary rock and speckled with vegetation. The multicolored surface may remind visitors of the Dakota Badlands, as may the surrounding treeless expanses. In a state full of natural wonders — from the jagged peaks of the Grand Tetons to the cylindrical monolith of Devils Tower — Fossil Butte is easily overlooked.
Moreover, this national monument in Wyoming's southwest corner is difficult to reach without a long drive in the backcountry. But intrepid travelers will be rewarded with big skies and eponymous fossils. And, like this underrated Wyoming state park that's a must-visit for wildlife lovers, Fossil Butte is a fantastic ecosystem for spotting wildlife.
The prehistoric origins of Fossil Butte
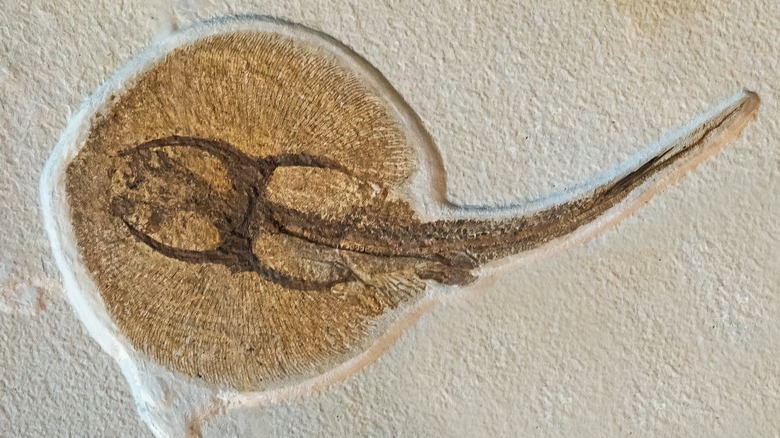
Animals have lived in this spot for at least 50 million years, but back then, most of its inhabitants had fins: the land mass that would become Fossil Butte lay was at the bottom of Fossil Lake. Over the eons, deceased marine specimens left permanent impressions in the emerging rock faces. Many of the fossils here are shockingly clear, giving scientists a vivid portrait of the sizes, shapes, and textures of various lifeforms.
So far, paleontologists have identified 27 fish species and 100 different kinds of insects. The Fossil Butte visitor center displays more than 2,000 of the fossils discovered here, including the "fish wall," "turtle wall," and "insect end case." The center also has an extended physical timeline, representing different stages of geology since Earth was formed, helping patrons appreciate just how ancient this region is.
If you're looking for fauna that still roams these parts, head outside. The grounds are crisscrossed with two main hiking routes: Historic Quarry Trail and Fossil Butte Nature Trail. Together, the trails cover about four miles and are well-maintained. More rustic alternatives include Cundick Ridge Trail, Eagle Nest Point Trail, and Rubey Point Trail. None of these trails is too difficult, and you'd be hard-pressed to get lost in such a wide-open space, but do make sure to bring water, snacks, and sunscreen, especially on hot days. (These are some of the hiking safety tips everyone should know.) From the trail, you're likely to spot pronghorns in the surrounding grasses, as well as white-tailed prairie dogs and ground squirrels. You're less likely to encounter a bobcat, mountain lion, moose, or badger, but rest assured, they're out there.
Getting to Fossil Butte and where to stay
Fossil Butte is definitely off the beaten path. Two hundred miles south of Yellowstone National Park and more than 350 miles from Wyoming's state capital Cheyenne, this national monument requires effort to visit. Interestingly, Fossil Butte is closer to Salt Lake City, Utah than it is to any major Wyoming destination, and you can drive from that city's airport — a major hub — to the entrance of Fossil Butte in a little over two hours.
This is a great location to get away from it all; the landscapes from the highway are rugged desert and prairie as far as the eye can see. You can drive for miles without passing so much as a service station. You could easily weave Fossil Butte into a scenic road trip from Salt Lake City to Yellowstone National Park. One consolation for venturing out so far is that entrance to Fossil Butte is free.
The closest hotels to the national monument are nestled in the little town of Diamondville. This place doesn't have quite 700 residents, but the nearby tourist attraction supports several accommodations, most under $100 per night. Note that Diamondville isn't next door; you'll have to drive about 12 miles to reach town, so keep an eye on that fuel gauge. If you come during warmer months, you can hop over to Bear Lake State Park in Utah, a popular spot for swimming and water-sports. It may give you an idea what Fossil Lake looked like all those ages ago.